The Vital Shield: Why Weld Passivation Matters for Stainless Steel
The Vital Shield: Why Weld Passivation Matters for Stainless Steel
Stainless steel, with its sleek shine and inherent resistance to corrosion, is a popular material for various applications. However, welding, a crucial joining process, can disrupt the natural protective layer on the steel, making it vulnerable to rust and degradation. This is where weld passivation comes in, acting as a vital shield to restore and enhance the steel's corrosion resistance.
What is Weld Passivation?
Imagine a thin, invisible film of chromium oxide naturally present on stainless steel. This film, formed by the interaction of chromium in the steel with oxygen, is the key to its corrosion resistance. Welding disrupts this film, exposing the underlying iron and jeopardizing the steel's protective barrier.
Weld passivation is a chemical or electrochemical process that removes contaminants and restores the chromium oxide layer on the welded areas. This newly formed layer is denser and more robust, providing superior protection against corrosion, pitting, and staining.
Benefits of Weld Passivation:
-
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: The primary benefit of weld passivation is significantly improved corrosion resistance. This is crucial for applications where stainless steel is exposed to harsh environments, such as chemical processing, marine environments, and food and beverage industries.
-
Extended Lifespan: By protecting against corrosion, weld passivation extends the lifespan of stainless steel components and structures. This translates to reduced maintenance costs and replacement needs.
-
Improved Aesthetics: Passivation removes discoloration and heat tint caused by welding, restoring the original bright and polished finish of the stainless steel. This is particularly important for architectural and decorative applications.
-
Enhanced Hygiene: In food and beverage processing, passivation minimizes the risk of bacteria and contaminant buildup on weld surfaces, promoting hygiene and safety.
-
Reduced Maintenance: The smooth, passivated surface is easier to clean and maintain, minimizing the need for harsh chemicals and frequent cleaning.
Weld Passivation Methods:
There are two main methods for weld passivation:
- Chemical Passivation: This method involves immersing the welded parts in a nitric acid solution. The acid dissolves contaminants and promotes the formation of a new chromium oxide layer.
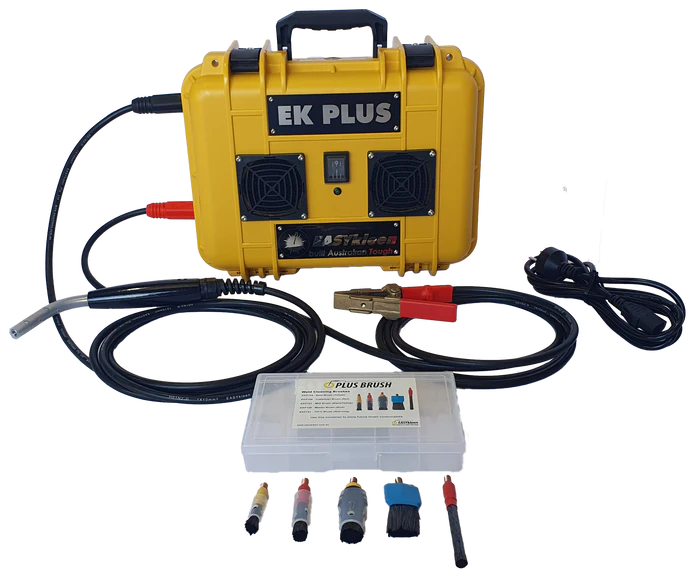
- Electrochemical Passivation: This method uses an electric current to remove contaminants and promote passivation. This method is often preferred for complex geometries and internal weld surfaces.
Choosing the Right Method:
The choice of passivation method depends on various factors, including the type of stainless steel, the size and complexity of the welds, and the desired level of finish. Consulting with a qualified professional is recommended to determine the most suitable method for your specific needs.
Conclusion:
Weld passivation is a critical step in ensuring the longevity and performance of stainless steel structures and components. By restoring and enhancing the natural protective layer, passivation provides significant benefits in terms of corrosion resistance, aesthetics, hygiene, and maintenance. For applications where stainless steel's integrity is paramount, weld passivation is an investment worth considering.
I hope this informative article has shed light on the importance of weld passivation for stainless steel. Remember, a little proactive care can go a long way in protecting your valuable stainless steel assets.

Leave a comment